Want to create hardcover books that readers will treasure? This comprehensive guide dives deep into hardcover book production, from anatomy and design to quality control and cost considerations. Learn the secrets to crafting high-quality, successful hardcover publications.
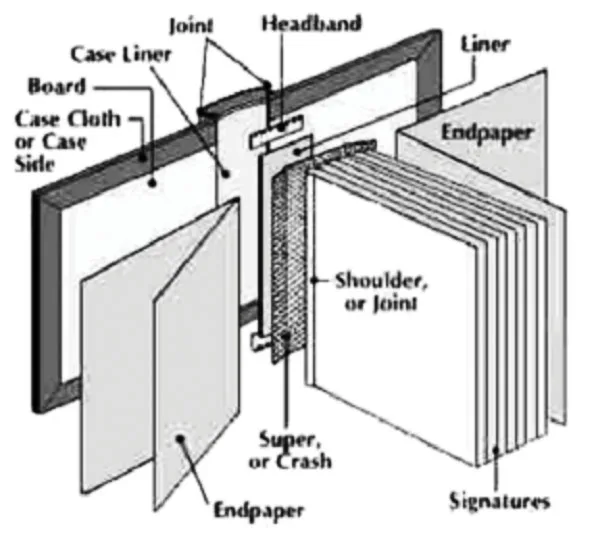
A hardcover book (also known as hardback, hardbound, or casebound) is a type of book bound with rigid protective covers. These covers are typically made of thick cardboard covered with cloth, heavy paper, or sometimes leather. Hardcover books are known for their durability, longevity, and aesthetic appeal. They often feature elements like a dust jacket, endpapers, and headbands for added protection and visual enhancement.
Discover the different types of hardcover books, the step-by-step production process, essential design principles, and key quality standards. Plus, we’ll explore the future of hardcover books in the digital age and provide expert insights to help you make informed publishing decisions.
Anatomy of a Hardcover Book
Think of a hardcover book as a finely crafted machine, with each part playing a crucial role in its overall form and function. Let’s break down the key components:
Boards (The Case)
The boards, or case, form the sturdy foundation of a hardcover book. They’re typically made of thick cardboard, providing rigidity and protection for the delicate pages within. You’ll often encounter two main types:
- Binder’s board: This classic choice is known for its durability and smooth surface, making it ideal for various cover materials.
- Greyboard: A more economical option, greyboard is often used for books with paper-over-board covers.
The thickness of the boards can vary, influencing the book’s weight and overall feel. Thicker boards generally provide greater durability, which is essential for books intended for heavy use, like those destined for libraries.
The Spine
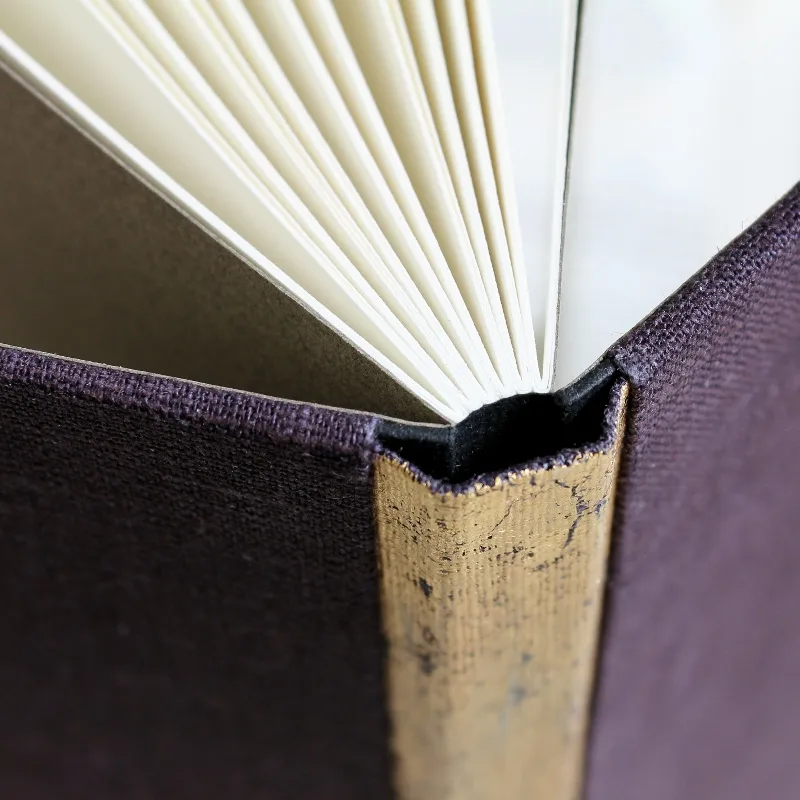

The spine is the backbone of the book, literally! It connects the front and back covers, providing structure and allowing the book to open and close. Spines come in different styles:
- Straight Spine: This classic style is common in many hardcover books.
- Rounded Spine: Often found in thicker books, a rounded spine provides extra flexibility and allows the book to lie flat when open.
The spine also serves as prime real estate for displaying the book’s title and author’s name, making it a key element in the book’s overall design.
Cover Material

The cover material is the face of the book, the first thing readers see and touch. It plays a crucial role in the book’s aesthetic appeal and perceived value. Common cover materials include:
- Cloth: Often made from buckram or linen, cloth covers offer a classic, elegant look and feel. They’re durable and can be easily embellished with foil stamping or embossing.
- Paper-over-board: A cost-effective option, this involves wrapping the boards with printed paper. It’s commonly used for trade hardcovers and offers a wide range of design possibilities.
- Leather: Reserved for high-end or special edition books, leather covers exude luxury and sophistication.
The choice of cover material depends on the book’s genre, target audience, and budget. For instance, a children’s book might benefit from a durable cloth cover, while a literary novel might opt for the classic elegance of paper-over-board.
Endpapers

Endpapers are like the hidden gems of a hardcover book. They’re the sheets of paper that connect the cover to the first and last pages of the book block. While often overlooked, endpapers can add a touch of elegance and personality to the book. They can be plain or decorated with patterns, illustrations, or even maps.
Headbands and Tailbands
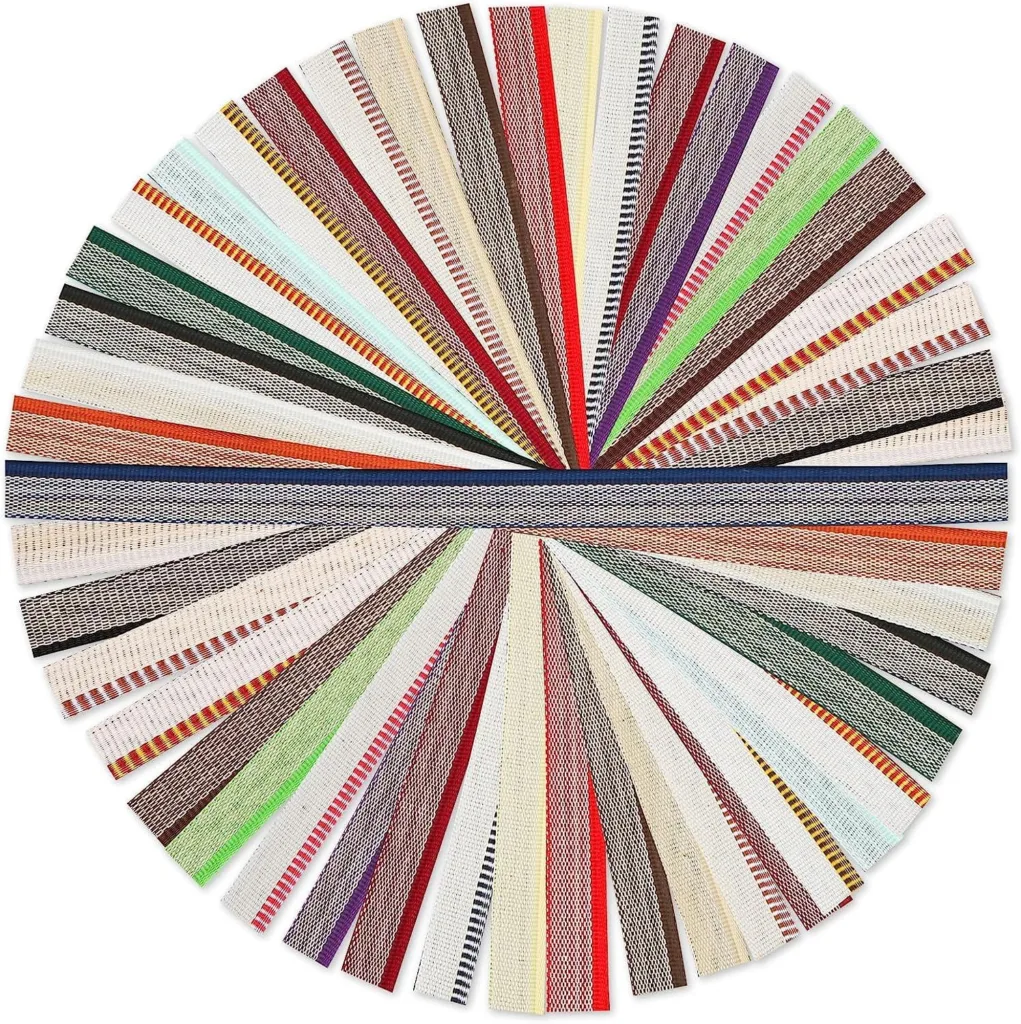

Headbands and tailbands are those decorative fabric strips you see at the top and bottom of the spine. They add a touch of refinement and help protect the spine from wear and tear. Traditionally, they were functional, reinforcing the spine, but today they primarily serve an aesthetic purpose.
The Dust Jacket
Ah, the dust jacket! This removable paper cover serves a dual purpose: it protects the book from dust and damage (hence the name), and it’s a powerful marketing tool. The dust jacket often features eye-catching artwork, a compelling blurb, and information about the author.
The flaps of the dust jacket are also important. The front flap typically provides a summary of the book, while the back flap often includes an author bio.
Think of the dust jacket as the book’s first impression. It’s the first thing potential readers see, and it can make or break their decision to pick up the book.
Types and Classification of Hardcover Books
Just like there’s no single “type” of reader, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to hardcover books. They come in a variety of styles and categories, each with its own unique characteristics and purpose.
Binding Methods
The binding is the heart of a hardcover book, holding the pages securely and allowing the book to open and close smoothly. Here are the most common binding methods used for hardcover books:
-
Case Binding: This is the gold standard for hardcover books. It involves sewing the pages together to form a text block, which is then glued to the cover boards. Case binding offers exceptional durability and allows the book to lay flat when open, making it ideal for textbooks, art books, and other publications where readers might need to refer to the pages frequently.
-
Smyth Sewn Binding:
Smyth Sewn Binding Known for its strength and longevity, Smyth sewn binding involves sewing groups of pages (called signatures) together and then sewing those signatures to the cover. This method is often used for high-quality books that are expected to withstand heavy use.
-
Perfect Binding:
Perfect Binding While more commonly associated with paperbacks, perfect binding can also be used for hardcover books, especially those with lower page counts. It involves roughening the spine of the text block and gluing the cover to it. While cost-effective, perfect binding may not be as durable as case binding or Smyth sewn binding.
Categories of Hardcover Books
Hardcover books can be broadly categorized based on their intended use and features:
-
Trade Hardcovers: These are the most common type of hardcover books you’ll find in bookstores. They’re designed for general readership and typically feature a dust jacket and standard cover materials like cloth or paper-over-board.
-
Library Bindings: As the name suggests, these hardcovers are specifically designed for libraries. They’re reinforced with extra durable materials and construction to withstand frequent handling and use.
-
Deluxe Editions: These are special editions of books that often feature premium materials, unique design elements, and extra features like slipcases or ribbon markers. They’re often produced in limited quantities and cater to collectors and bibliophiles.
Understanding the different binding methods and categories of hardcover books will help you make informed decisions about the best approach for your specific publication. To further explore the choice between hardcover and softcover, check out our detailed comparison in this article.
For instance, if you’re publishing a coffee table book with high-quality images, you might opt for a layflat binding to showcase the visuals effectively. On the other hand, a mass-market novel might be more suited to a standard case binding with a paper-over-board cover.
Hardcover Book Production Process
Table Title: Key Components of Hardcover Book Production
| Component | Description | Common Types/Materials | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boards (The Case) | The sturdy foundation of a hardcover book, providing rigidity and protection. | Binder’s board (durable, smooth surface), Greyboard (economical, used for paper-over-board) | Thickness affects weight and durability; thicker boards for heavy use like libraries. |
| Spine | Connects the front and back covers, allowing the book to open and close. | Straight Spine, Rounded Spine (flexible, allows flat opening) | Displays title and author’s name; rounded spine for thicker books. |
| Cover Material | The first impression, influencing aesthetic appeal and perceived value. | Cloth (buckram, linen), Paper-over-board, Leather (high-end) | Genre, target audience, budget; durability and design possibilities. |
| Endpapers | Connect the cover to the book block, adding elegance and personality. | Plain or decorated with patterns, illustrations, or maps | Enhance aesthetic appeal; can be used for thematic elements. |
| Headbands/Tailbands | Decorative fabric strips at the top and bottom of the spine. | Fabric materials | Aesthetic enhancement; traditional function was to reinforce the spine. |
| Dust Jacket | Removable paper cover for protection and marketing. | Paper with artwork, blurb, author bio | Attracts potential readers; provides book summary and author information. |
| Binding Methods | Holds the pages securely and allows smooth opening. | Case Binding, Smyth Sewn Binding, Perfect Binding | Durability, cost, and suitability for book type (e.g., textbooks, novels). |
| Interior Design | Enhances the reading experience with layout and formatting. | Page layout, chapter openings, image placement | Readability, consistency, and visual appeal. |
| Quality Standards | Ensures the book’s durability and aesthetic appeal. | Cover durability, binding strength, paper quality, printing accuracy | Rigorous quality control checks throughout the production process. |
Creating a hardcover book is a journey that involves multiple steps, each requiring precision and expertise. Let’s take a behind-the-scenes look at the typical hardcover book production process:
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Manuscript Preparation: It all starts with a well-prepared manuscript. This involves meticulous editing, typesetting to ensure proper formatting and readability, and proofreading to catch any errors.
-
Printing: The printing stage brings the words and images to life on paper. The choice between offset printing and digital printing depends on factors like the quantity of books needed and the desired quality level.
Offset printing is generally more cost-effective for larger print runs, while digital printing offers flexibility for smaller quantities and quicker turnaround times. You can learn more about the differences between offset and digital printing in our article.
-
Binding: The printed pages are gathered into signatures (groups of folded pages), which are then sewn together to create a text block. The spine is prepared, and the text block is glued to the cover boards, completing the binding process.
-
Cover Creation: The cover is crafted separately, starting with cutting the boards to the desired size. The chosen cover material (cloth, paper, or leather) is then wrapped around the boards, and any decorative elements like foil stamping or embossing are applied.
-
Quality Control: Throughout the entire process, rigorous quality control checks are performed to ensure that the final product meets the highest standards. This involves inspecting the books for any defects, such as warped covers, loose pages, or printing errors. You can learn more about quality control in book printing.
This multi-stage process requires close collaboration between authors, editors, designers, printers, and binders. Each step plays a vital role in creating a hardcover book that is both beautiful and durable.
To delve deeper into the intricacies of hardcover book printing, check out our comprehensive guide.
Design Principles and Best Practices
A well-designed hardcover book is a feast for the eyes and a joy to hold. But it’s not just about aesthetics; effective design also plays a crucial role in conveying the book’s message and attracting readers. Let’s explore some key design principles and best practices:
Cover Design
The cover is the book’s first impression, and it needs to be captivating. Here are some essential elements to consider:
-
Typography: Choosing the right fonts is crucial for readability and visual appeal. Consider the book’s genre and target audience when selecting fonts. For example, a classic serif font might be appropriate for a literary novel, while a bold sans-serif font might be a better choice for a contemporary thriller.
-
Imagery: If you’re using images on the cover, ensure they are high-quality, relevant to the book’s content, and visually striking.
-
Color Palette: Colors evoke emotions and set the tone for the book. Choose a color palette that aligns with the book’s genre and target audience.
-
Finishing Techniques: Embossing, debossing, and foil stamping can add a touch of luxury and sophistication to the cover. These techniques can highlight key design elements and create a tactile experience for the reader. For inspiration and examples, explore this showcase of stunning hardcover book cover designs on Printivity.
Interior Design
The interior design of a hardcover book should complement the cover and enhance the reading experience. Here are some key considerations:
-
Page Layout: Pay attention to margins, white space, and typography to create a visually appealing and easy-to-read layout.
-
Chapter Openings: Design chapter openings with care, using consistent elements to create a sense of flow and hierarchy.
-
Image Placement: If the book includes images, ensure they are placed thoughtfully and accompanied by clear and informative captions.
By following these design principles and best practices, you can create hardcover books that are both visually stunning and engaging for readers. Remember, the design should not only be beautiful but also serve the book’s content and purpose.
Quality Standards and Control
In the world of publishing, quality is paramount. A poorly made hardcover book can disappoint readers and damage a publisher’s reputation. That’s why maintaining high quality standards and implementing rigorous quality control measures are essential throughout the entire production process.
Key Quality Indicators
When assessing the quality of a hardcover book, pay close attention to these key indicators:
-
Cover Durability: The cover should be sturdy and resistant to wear and tear. It should withstand normal handling without showing signs of damage or warping.
-
Binding Strength: The pages should be securely bound to the cover, with no signs of looseness or detachment. The spine should be flexible enough to allow the book to open and close smoothly but strong enough to prevent pages from falling out.
-
Paper Quality: The paper should be of appropriate weight and opacity, ensuring that the text is legible and the images are clear. The paper should also have a pleasant texture that enhances the reading experience.
The selection of paper is also crucial at this stage, considering factors like weight, opacity, and texture. You can find more information about different paper types for book printing. -
Printing Accuracy: The printing should be accurate and consistent, with no color variations or misregistration. The text should be sharp and clear, and the images should be reproduced faithfully.
Common Defects and Solutions
Even with the best intentions and processes, quality issues can sometimes arise. Here are some common defects to watch out for and tips on how to address them:
-
Warped Covers: This can occur due to moisture or improper storage. Ensure that the books are stored in a dry and climate-controlled environment.
-
Loose Pages: This can be caused by inadequate glue or stitching during the binding process. Work with your printer to ensure that the binding is secure.
-
Printing Errors: These can range from minor typos to major color inconsistencies. Implement a thorough proofreading process and work closely with your printer to ensure that the printing meets your specifications.
By adhering to quality standards and implementing effective quality control measures, you can ensure that your hardcover books are not only beautiful but also built to last.
Cost Considerations and Pricing Strategies
Producing hardcover books involves various costs, from materials and printing to binding and finishing. Understanding these costs and implementing effective pricing strategies are crucial for ensuring profitability and market competitiveness.
Factors Affecting Cost
Several factors influence the cost of producing hardcover books:
-
Materials: The cost of materials can vary significantly depending on the type of board, cover material, and paper used. For instance, a book with a leather cover and high-quality paper will naturally be more expensive to produce than a book with a paper-over-board cover and standard paper.
-
Printing Method: Offset printing is generally more cost-effective for larger print runs, while digital printing is more suitable for smaller quantities. The choice of printing method can significantly impact the overall cost.
-
Binding Technique: Different binding techniques have different cost implications. Case binding, for instance, is typically more expensive than perfect binding due to the more complex process involved.
-
Finishing Options: Adding finishing touches like embossing, debossing, or foil stamping can increase the cost. The complexity and extent of the finishing will influence the final price.
-
Quantity: As with most things, economies of scale apply to book printing. Printing larger quantities generally results in a lower per-unit cost.
For a detailed breakdown of hardcover book printing costs, be sure to read our comprehensive guide.
Pricing Strategies
Setting the right price for your hardcover book is a balancing act. You need to consider the cost of production, the perceived value of the book, and the competitive landscape. Here are some key factors to consider:
-
Market Research: Analyze the pricing of similar books in the market to get a sense of what readers are willing to pay.
-
Perceived Value: Hardcovers are often perceived as more valuable than paperbacks due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. This allows for a higher price point.
-
Profit Margins: Ensure that your pricing strategy allows for a healthy profit margin while remaining competitive in the market.
Remember, the goal is to find a price that is attractive to readers while also ensuring that you can cover your costs and generate a reasonable profit.
Hardcover Books in the Digital Age
In today’s digital world, where e-books and audiobooks are readily available, you might wonder about the future of hardcover books. Are they destined to become relics of the past, or do they still hold a place in the hearts and hands of readers?
Challenges and Opportunities
The publishing industry has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, and hardcover books have faced their share of challenges:
-
E-book Growth: The rise of e-books has undoubtedly impacted the print book market, including hardcovers. E-books offer convenience, portability, and often lower prices, making them an attractive option for many readers.
-
Print-on-Demand: Print-on-demand technology has disrupted traditional printing models, allowing for smaller print runs and reducing the need for large inventories. While this offers flexibility, it can also impact the cost-effectiveness of hardcover production.
-
The Rise of Audiobooks: Audiobooks have gained immense popularity, offering a convenient way to consume books while multitasking. This has added another layer of competition for readers’ attention.
However, amidst these challenges, hardcover books also have unique opportunities:
-
Niche Markets: Hardcovers can thrive in niche markets, such as collector’s editions, limited print runs, and special interest publications.
-
Personalization and Customization: Advances in printing technology allow for greater personalization and customization of hardcover books, catering to individual preferences and creating unique, collectible items.
-
Sustainability: The publishing industry is increasingly embracing sustainable practices, and hardcover books can play a role in this movement by using eco-friendly materials and production methods.
The Future of Hardcover Books
Despite the challenges posed by the digital age, hardcover books are far from obsolete. They continue to hold a special place in the hearts of many readers, offering a tactile and sensory experience that digital formats simply cannot replicate.
As Michael Hyatt, Chairman of Michael Hyatt & Company and former CEO of Thomas Nelson Publishers, points out, “Hardcover books make a better first impression and are more likely to be kept and displayed by readers.” This highlights the enduring value and appeal of hardcovers in a world increasingly dominated by digital content.
Furthermore, hardcover books are likely to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape. We can expect to see more innovation in design, materials, and production methods, making them even more appealing and sustainable.
Conclusion: Hardcover Books – A Timeless Classic
So, there you have it – a comprehensive journey through the world of hardcover books. We’ve explored their anatomy, delved into the different types and production processes, uncovered design secrets, and even pondered their future in the digital age.
As publishing professionals, you play a crucial role in shaping the future of these enduring classics. By understanding the intricacies of hardcover book production and design, you can create high-quality, successful publications that captivate readers and stand the test of time.
Whether you’re working on a literary masterpiece, a coffee table book filled with stunning visuals, or a textbook designed for years of use, remember the importance of quality, craftsmanship, and attention to detail.
And as the publishing landscape continues to evolve, embrace innovation and explore new ways to make hardcover books even more appealing, sustainable, and relevant to today’s readers.
For a detailed comparison of paperback and hardback formats, you can read our in-depth analysis.
After all, as Joanna Penn, author and entrepreneur, wisely states in her book “Successful Self-Publishing,” “Hardcovers have a higher perceived value and collectability.” This enduring appeal ensures that hardcover books will continue to hold a special place in the world of publishing for years to come.
Resources
- Print Hardcover Book Cost: This resource explores the breakdown of costs associated with printing hardcover books.
- How to Print a Hardcover Book: A comprehensive guide on the process of printing hardcover books.
- Paperback vs Hardback: A detailed comparison of paperback and hardcover formats, highlighting their pros and cons.
- Hardcover vs Softcover: This comprehensive guide dives into the key differences between hardcover and softcover formats, helping you decide which one is best for your book.










